Custom Web Server
Modern.js encapsulates most server-side capabilities required by projects, typically eliminating the need for server-side development. However, in certain scenarios such as user authentication, request preprocessing, or adding page skeletons, custom server-side logic may still be necessary.
To use the Custom Web Server in a Modern.js project, follow these steps:
- Install
@modern-js/server-runtime dependency
If the @modern-js/server-runtime dependency is not yet installed in your project, install it first:
pnpm add @modern-js/server-runtime
Version Consistency
Make sure the version of @modern-js/server-runtime matches the version of @modern-js/app-tools in your project. All Modern.js official packages are released with a uniform version number, and version mismatches may cause compatibility issues.
Check the version of @modern-js/app-tools first, then install the same version of @modern-js/server-runtime:
# Check the current version of @modern-js/app-tools
pnpm list @modern-js/app-tools
# Install the same version of @modern-js/server-runtime
pnpm add @modern-js/server-runtime@<version>
- Create the
server directory and configuration file
Create a server/modern.server.ts file in the project root directory:
server/modern.server.ts
import { defineServerConfig } from '@modern-js/server-runtime';
export default defineServerConfig({
middlewares: [], // Middleware
renderMiddlewares: [], // Render Middleware
plugins: [], // Plugins
onError: () => {}, // Error handling
});
After creating the file, you can write custom logic in this file.
Capabilities of the Custom Web Server
Modern.js's Web Server is based on Hono, and in the latest version of the Custom Web Server, we expose Hono's middleware capabilities, you can refer to Hono API for more usage.
In the server/modern.server.ts file, you can add the following configurations to extend the Server:
- Middleware
- Render Middleware
- Server-side Plugin
In the Plugin, you can define Middleware and RenderMiddleware. The middleware loading process is illustrated in the following diagram:
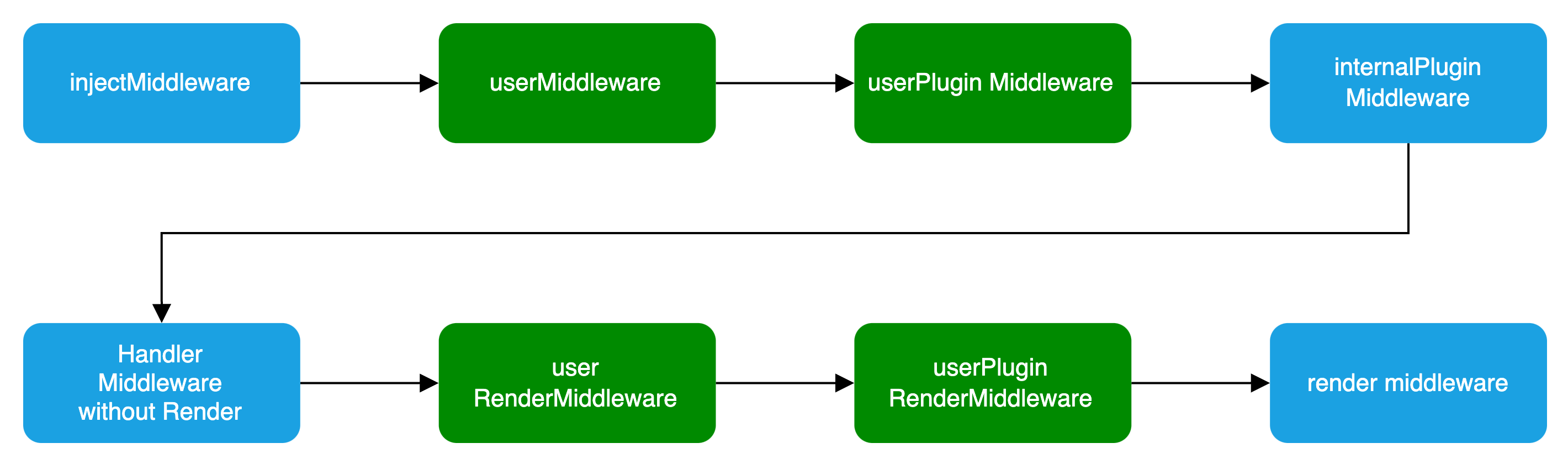
Basic Configuration
server/modern.server.ts
import { defineServerConfig } from '@modern-js/server-runtime';
export default defineServerConfig({
middlewares: [],
renderMiddlewares: [],
plugins: [],
onError: () => {},
});
Type Definition
defineServerConfig type definition is as follows:
import type { MiddlewareHandler } from 'hono';
type MiddlewareOrder = 'pre' | 'post' | 'default';
type MiddlewareObj = {
name: string;
path?: string;
method?: 'options' | 'get' | 'post' | 'put' | 'delete' | 'patch' | 'all';
handler: MiddlewareHandler | MiddlewareHandler[];
before?: Array<MiddlewareObj['name']>;
order?: MiddlewareOrder;
};
type ServerConfig = {
middlewares?: MiddlewareObj[];
renderMiddlewares?: MiddlewareObj[];
plugins?: ServerPlugin[];
onError?: (err: Error, c: Context) => Promise<any> | any;
};
Middleware
Middleware supports executing custom logic before and after the request handling and page routing processes in Modern.js services.
If custom logic needs to handle both API routes and page routes, Middleware is the clear choice.
Note
If you only need to handle BFF API routes, you can determine whether a request is for a BFF API by checking if req.path starts with the BFF prefix.
Usage is as follows:
server/modern.server.ts
import {
defineServerConfig,
type MiddlewareHandler,
} from '@modern-js/server-runtime';
export const handler: MiddlewareHandler = async (c, next) => {
const monitors = c.get('monitors');
const start = Date.now();
await next();
const end = Date.now();
// Report Duration
monitors.timing('request_timing', end - start);
};
export default defineServerConfig({
middlewares: [
{
name: 'request-timing',
handler,
},
],
});
Warning
You must execute the next function to proceed with the subsequent Middleware.
RenderMiddleware
If you only need to handle the logic before and after page rendering, modern.js also provides rendering middleware, which can be used as follows:
server/modern.server.ts
import {
defineServerConfig,
type MiddlewareHandler,
} from '@modern-js/server-runtime';
// Inject render performance metrics
const renderTiming: MiddlewareHandler = async (c, next) => {
const start = Date.now();
await next();
const end = Date.now();
c.res.headers.set('server-timing', `render; dur=${end - start}`);
};
// Modify the Response Body
const modifyResBody: MiddlewareHandler = async (c, next) => {
await next();
const { res } = c;
const text = await res.text();
const newText = text.replace('<body>', '<body> <h3>bytedance</h3>');
c.res = c.body(newText, {
status: res.status,
headers: res.headers,
});
};
export default defineServerConfig({
renderMiddlewares: [
{
name: 'render-timing',
handler: renderTiming,
},
{
name: 'modify-res-body',
handler: modifyResBody,
},
],
});
Plugin
Modern.js supports adding the aforementioned middleware and rendering middleware for the Server in custom plugins, which can be used as follows:
server/plugins/server.ts
import type { ServerPlugin } from '@modern-js/server-runtime';
export default (): ServerPlugin => ({
name: 'serverPlugin',
setup(api) {
api.onPrepare(() => {
const { middlewares, renderMiddlewares } = api.getServerContext();
// Inject server-side data for page dataLoader consumption
middlewares?.push({
name: 'server-plugin-middleware',
handler: async (c, next) => {
c.set('message', 'hi modern.js');
await next();
// ...
},
});
// redirect
renderMiddlewares?.push({
name: 'server-plugin-render-middleware',
handler: async (c, next) => {
const user = getUser(c.req);
if (!user) {
return c.redirect('/login');
}
await next();
},
});
});
},
});
server/modern.server.ts
import { defineServerConfig } from '@modern-js/server-runtime';
import serverPlugin from './plugins/serverPlugin';
export default defineServerConfig({
plugins: [serverPlugin()],
});
src/routes/page.data.ts
import { useHonoContext } from '@modern-js/server-runtime';
import { defer } from '@modern-js/runtime/router';
export default () => {
const ctx = useHonoContext();
// SSR scenario consumes data injected by the Server Side
const message = ctx.get('message');
// ...
};
onError
onError is a global error handling function used to capture and handle all uncaught errors in the Modern.js server. By customizing the onError function, developers can uniformly handle different types of errors, return custom error responses, and implement features such as error logging and error classification.
Below is a basic example of an onError configuration:
server/modern.server.ts
import { defineServerConfig } from '@modern-js/server-runtime';
export default defineServerConfig({
onError: (err, c) => {
// Log the error
console.error('Server error:', err);
// Return different responses based on the error type
if (err instanceof SyntaxError) {
return c.json({ error: 'Invalid JSON' }, 400);
}
// Customize BFF error response based on request path
if (c.req.path.includes('/api')) {
return c.json({ message: 'API error occurred' }, 500);
}
return c.text('Internal Server Error', 500);
},
});

